| Name | Functional Group Structure | Example Compound | Official Name of Example (Common Name) Formal Name Ending |
| alkane | none (all carbon-carbon single bonds) | 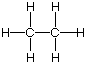
| ethane (ethane) -ane endings |
Alkanes |
| Name | Functional Group Structure | Example Compound | Official Name of Example (Common Name) Formal Name Ending |
| alkane | none (all carbon-carbon single bonds) | 
| ethane (ethane) -ane endings |
| Name | Formula | Name | Formula | |
| methane | CH4 | pentane | C5H12 | |
| ethane | C2H6 | hexane | C6H14 | |
| propane | C3H8 | heptane | C7H16 | |
| butane | C4H10 | octane | C8H18 |
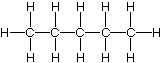 is pentane
is pentane
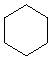 is cyclohexane
is cyclohexane

| introduction | background | prelab | experiment | postlab |